
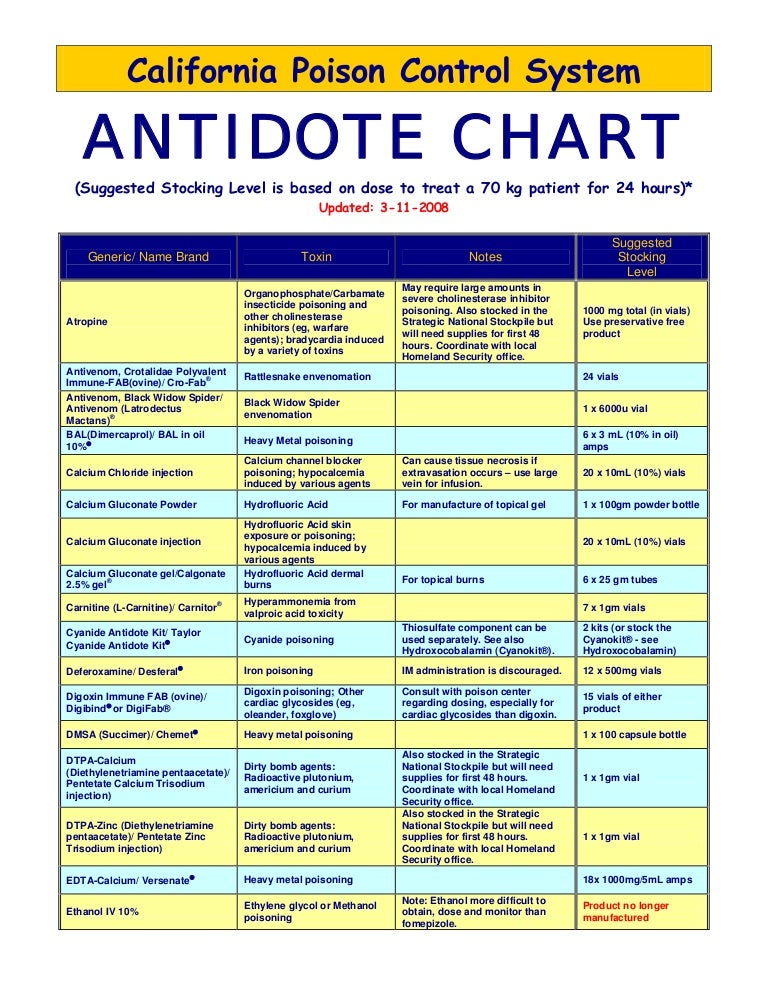
For example, aPTT prolongation by betrixaban (400nM) was reversed with an estimated EC 50=650nM. In an activated partial thromboplastin time assay (aPTT), pd-Antidote also dose-dependently reversed the inhibitory effects of the fXa inhibitors. Addition of pd-Antidote (515nM) produced a 37% reduction of the clotting activity of enoxaparin (1.25Units/ml). Pd-Antidote also demonstrated reversal of the in-vitro anticoagulant activity of the LMWH, enoxaparin. In a tissue factor-initiated thrombin generation assay in plasma, while pd-Antidote did not interfere with the normal function of prothrombinase complexes, it dose-dependently and completely reversed the inhibition produced by the small molecule fXa inhibitors. The activity of pd-Antidote was not limited to reversal of purified fXa catalytic activity. Thus, active site inactivated pd-Antidote retained the ability to bind small molecule inhibitors of fXa.
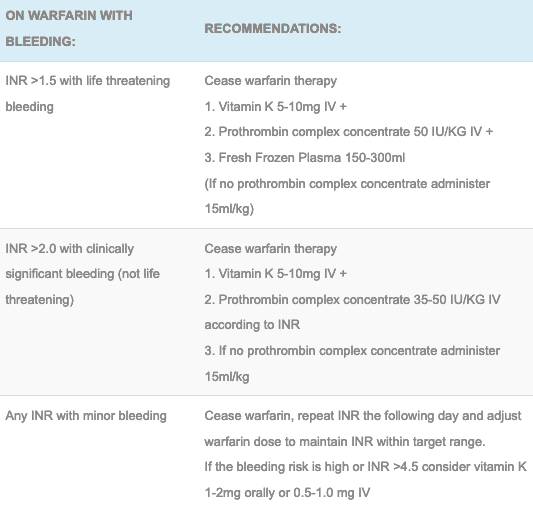
The pd-Antidote had no effect on the activity of fXa in the absence of inhibitors. In a fXa amidolytic assay with 3nM enzyme, half maximal reversal of inhibitory activities (EC 50) was attained at the following pd-Antidote concentrations: rivaroxaban =49 nM, apixaban = 122 nM, betrixaban = 41 nM. Preliminary experiments showed that pd-Antidote dose dependently reversed the activity of rivaroxaban, apixaban or betrixaban, three small molecule fXa inhibitors currently in clinical trials. Plasma derived antidote (pd-Antidote) was prepared by chemical modification of the active site serine of fXa followed by chymotryptic removal of the Gla domain. The present study was designed to test the hypothesis that plasma-derived or recombinant fXa, modified to lack catalytic and membrane binding activities, could neutralize the anticoagulant activities of small molecule fXa inhibitors and LMWH. In contrast, specific and effective antidotes are not available for the reversal of the anticoagulant effects of the low molecular weight heparins (LMWH) or the new oral anticoagulants targeting factor Xa (fXa) which are predictably only marginally affected by standard treatments using rfVIIa or fresh frozen plasma. Individuals anticoagulated with warfarin or heparin are typically treated with specific antidotes such as vitamin K or protamine, respectively, if they bleed or require surgery.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
